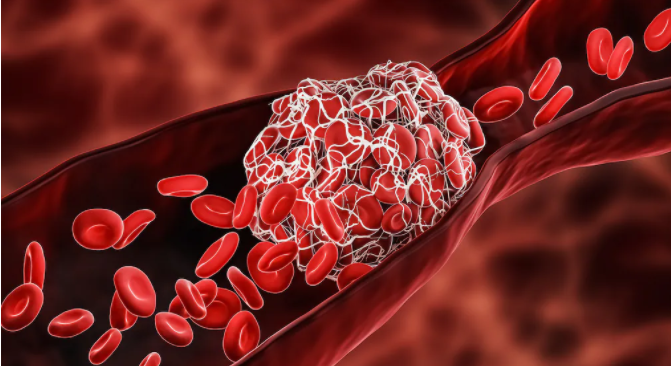
The chance of a blood coagulation isn’t typically on the personalities of the vast majority when they focus in for an antibody, however recently that issue has been on the radar.
As of late, immunizations with the AstraZeneca COVID-19 shot were required to be postponed in nations across Europe following reports of uncommon blood clumps, low platelets, and drain. After conventional survey, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and World Health Organization (WHO) both gave explanations saying that the general danger for coagulating with this antibody is no higher than in everybody, that the advantages exceed the dangers, and that inoculations should proceed. The American Society of Hematology has likewise said that the advantages of the AstraZeneca antibody exceed thickening danger.
The AstraZeneca COVID Vaccine
The EMA and WHO explored 18 instances of cerebral venous sinus apoplexy (CVST) following organization of more than 20 million dosages of the AstraZeneca immunization. Practically these occasions occurred in ladies under age 55. CVST alludes to clumps framing in veins that channel the cerebrum, which can prompt drain and stroke. It is uncommon, and typically influences around 5 individuals in 1 million every year.
“CVST is one of those low recurrence, high dreariness conditions that stands out,” said Rajiv Pruthi, MBBS, a hematologist at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
In its assertion, the EMA said that “a few concerns” stay for uncommon instances of explicit apoplexies in more youthful individuals, and that the antibody item data ought to be refreshed to incorporate the likelihood that uncommon, explicit apoplexies may happen as long as 16 days after inoculation. Both WHO and the EMA have said that further examination is justified.
In AstraZeneca’s declaration of topline break results from its U.S. preliminary, the organization said it searched explicitly for CVST cases among members and there were none. Around 32,500 individuals were in the preliminary, including more than 20,000 accepting the immunization.
Clumps in the U.S.
In the U.S., a Miami doctor passed on after confusions of insusceptible thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) after his first portion of the Pfizer COVID-19 immunization. ITP is an uncommon immune system condition in which the body produces autoantibodies to its own platelets, bringing about low platelet checks, blood clumps, and draining if the platelet tally drops low. Around 50,000 grown-ups are determined to have ITP in the U.S. each year. Hazard is expanded in young ladies and individuals with other immune system conditions.
For a situation arrangement, James Bussel, MD, and partners audited 20 reports of thrombocytopenia after receipt of the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 immunizations in the U.S. Bussel is educator emeritus of pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York City who has distributed broadly on ITP. His gathering tracked down that 17 of these patients didn’t have prior thrombocytopenia. Patients’ middle age was 41 and 11 were ladies.